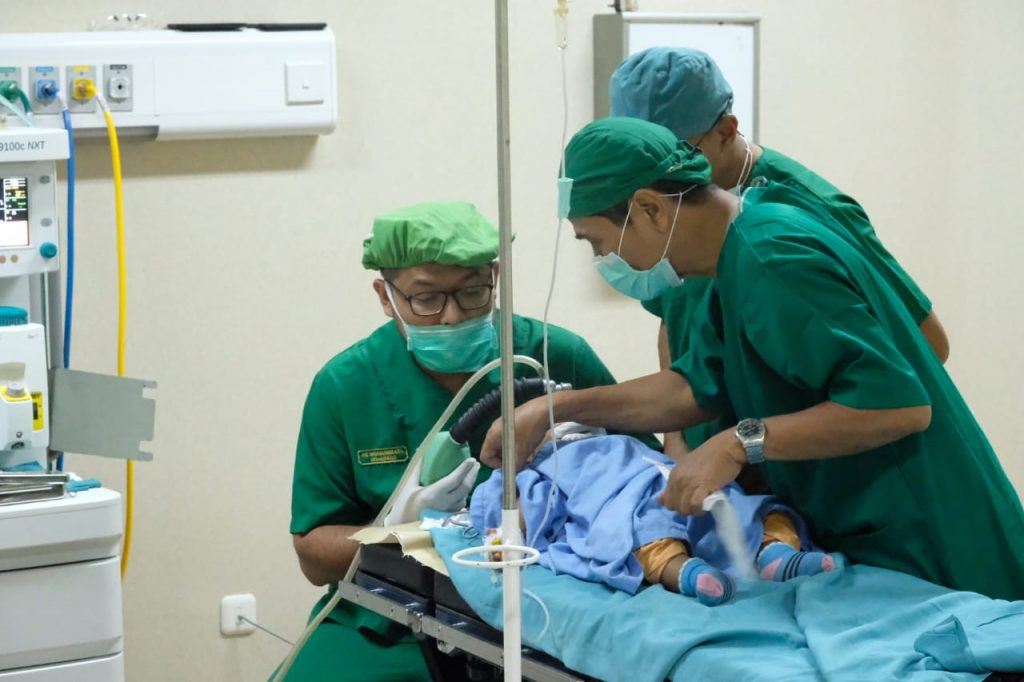
Cleft lip surgery to improve the shape of the lip and nose (nasolabial) area is sometimes followed with some complaints, such as asymmetrical lips and nose. As a surgeon, you must know how to assess these complaints objectively. Several studies have suggested several measuring devices such as the use of photographs, both two-dimensional and three-dimensional, use of video, and measurements directly to the patient’s face.
The latest measurement method from Americleft called “Expanded Nasolabial Americleft Yardstick” stated that it has a high level of reliability. Americleft Yardstick assessed the results of cleft lip operation using two-dimensional photographs from the front and sides. However, the Americleft yardstick does not include one parameter, “Basal View”. Basal View is a photo of the patient from the bottom where the nose position can be seen more clearly.
Our team often finds patients’ complaints about their asymmetrical noses when they look at the mirror and looking at them from the bottom. Therefore, our team assumes that “Basal View” has value in evaluating the results of cleft surgery. To answer that question, we designed a study comparing the original Americleft Yardstick and with the addition of Basal View of patients in Japan.
Our data was collected from photos of patients 5-7 years old after cleft lip surgery. Data collected were from patients with unilateral cleft lip. The used photos are a photo from the front and from the side. The assessment uses a scale of 1-5, where 1 is the best and 5 is the worst.
The elements assessed from the front photo were the Nasolabial frontal (NLF) and the vermilion border (VB) while the element assessed from the side photo is a nasolabial profile (NLP). Then we compare these values with the addition of the basal view (BV) value. The assessment was carried out twice by three surgeons in a span of two weeks.
The results showed that the average total value between the Americleft Method and the Americleft Method plus Basal View is not significantly different in the range 2-3. The scores between the three assessors also showed no difference. We calculated the reliability using a kappa score, where our results showed “Moderate” reliability in both assessment methods. Next, we calculated the correlation between each element of assessment from Americleft and the value of “Basal View”. Strong positive correlation was shown by the element of frontal nasolabial assessment (NLF) with basal view (BV).
Within limits, the conclusion of this study showed that Americleft Yardstick can be used with moderate reliability. The existence of ambiguity in the NLP element, may be the cause of the decreased reliability of Americleft Yardstick when it is used to Japanese patient population.
The addition of “Basal View” element to the Americleft Yardstick does not seem to have any significant difference in the overall assessment. However, further research with a larger sample size must be carried out to answer this. (*)
Author: Muhammad Subhan Amir
Details of research available at: