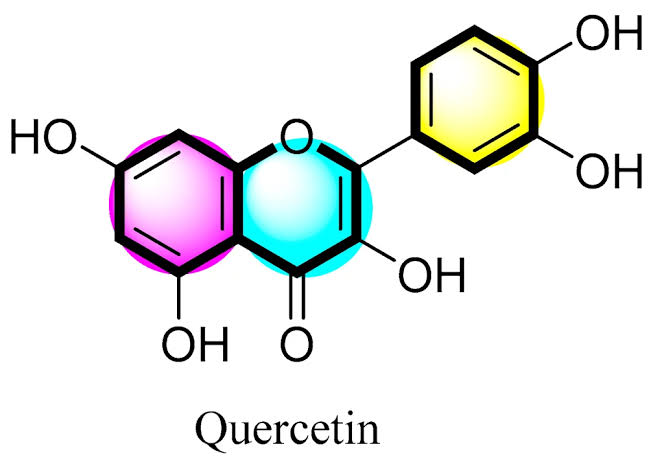
The purpose of this study was to determine characteristics and release of quercetin microspheres with a matrix of sodium alginate-chitosan combination by studying the effect of chitosan concentration. The ability of the drug to release from the microsphere matrix is one of the factors that influence its effectiveness as an immunomodulator. Therefore, a drug release test was carried out for 8 hours at a pH of 6.0, which is the intestinal pH where quercetin is maximally absorbed. The method of producing microspheres is ionotropic gelation aerosolization technique, and characterization includes particle size, entrapment efficiency, drug loading and release study.
Three formulas were created each with a Na-Alginate concentration of 2 % and a chitosan concentration of F1 (0 %), F2 (0.5%), and F3 (1.0%) with a 0.5M CaCl2 cross-linking solution. Results of particle size of F1 (2.67± 0.09) μm, F2 (2.72±0.06) μm, F3 (3.02±0.11)μm, entrapment efficiency of F1 (87.32 ± 0.78)%, F2 (89.01± 2.50)%, F3 (94.70±0.78) %, drug loading of F1 (8.21±0.31)%, F2 (6.14 ± 0.26)%, F3 (4.73±0.35)%, and swelling index at the 1st hour in pH 6 of F1 (628.76±41.51)%, F2 (614.44 ± 55.53)%, F3 (310.43±32.50)%.
Increased chitosan concentrations (0%, 0.5%, and 1.0%) resulted in increasingly compact, spherical quercetin microspheres with smooth surfaces, increasing particle size, increasing yield value, moisture content, entrapment efficiency, but lowering drug loading. The swelling process lasts longer and the release time is extended.
Author: Dewi Melani Hariyadi
Details can be accessed from the link below: https://www.rjptonline.org/AbstractView.aspx?PID=2025-18-1-7